A research team led by Prof. YANG Xueming from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reviewed the progress of Single Molecule Photocatalysis on TiO2 Surfaces. The article was published in Chemical Reviews.
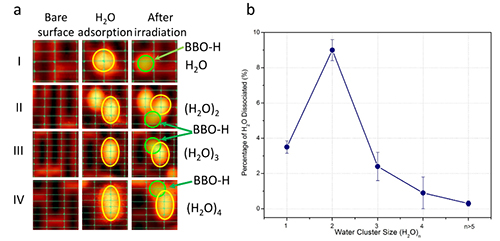
STM images of the photolysis of H2O monomer, dimer, trimer and tetramer on R-TiO2(110) under 266 nm irradiation (Image by GUO Qing)
Heterogeneous photocatalysis has been widely applied in various fields, such as photovoltaic cell, solar water splitting, photocatalytic pollutant degradation, and so on. Therefore, the reaction mechanisms involved in these important photocatalytic processes, especially in TiO2 photocatalysis, have been extensively investigated by various surface science techniques in the past decade.
In this review, Scientists summarized the recent progress that provides fundamental insights into TiO2 photocatalysis through direct tracking the evolution of single molecule photochemistry on TiO2 single crystal surfaces using a combination of scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) and other surface science techniques.
The details of the single molecule photocatalysis of several important molecules (water, alcohols, and aldehydes) on the model TiO2 surfaces were highlighted, and perspectives on single molecule photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces in the future were provided.
The above work was supported was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC Center for Chemical Dynamics, 21673235), the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB17000000), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (Text by GUO Qing)