Research News
-
 04 16, 2019Activation of AMPK Depends on Severity of Nutrient or Energy StressScientists discovered that Hierarchical activation of AMPK depended on severity of nutrient or energy stress.
04 16, 2019Activation of AMPK Depends on Severity of Nutrient or Energy StressScientists discovered that Hierarchical activation of AMPK depended on severity of nutrient or energy stress.
Recently, scientists from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. LIN Sheng-Cai from Xiamen University and Prof. D. Grahame Hardie from the University of Dundee, discovered that hierarchical activation of AMPK depended on severity of nutrient or energy stress. Their findings were published in Cell Research.
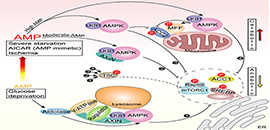
A simplified model depicting that the differentially compartmentalized pools of AMPK are activated with different dependencies on AXIN, and the severities of nutrient or energy stress. (Image by WANG Wen and WANG Ting)
AMPK, a master regulator of metabolic homeostasis, is activated by both AMP-dependent and AMP-independent mechanisms. The conditions under which these different mechanisms operate, and their biological implications are unclear.
Depending on the degree of elevation of cellular AMP, the scientists found that distinct compartmentalized pools of AMPK were activated, phosphorylating different sets of targets.
Low glucose activated AMPK exclusively through the AMP-independent, AXIN-based pathway in lysosomes to phosphorylate targets such as ACC1 and SREBP1c, exerting early anti-anabolic and pro-catabolic roles.
Moderate increased in AMP expanded this to activate cytosolic AMPK also in an AXIN-dependent manner. In contrast, high concentrations of AMP, arising from severe nutrient stress, activated all pools of AMPK independently of AXIN.
These findings revealed a spatiotemporal basis for hierarchical activation of different pools of AMPK during differing degrees of stress severity.
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology, Xiamen University. (Text by Wen Wang and WANG Ting) -
 04 10, 2019Scientists Realize Biomimetic Prenylation and Reverse-Prenylation of Indoles with IsopreneRecently, a team led by Prof. CHEN Qing-An from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed biomimetic prenylation and reverse-prenylation of indoles with isoprene. Their findings were published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed..
04 10, 2019Scientists Realize Biomimetic Prenylation and Reverse-Prenylation of Indoles with IsopreneRecently, a team led by Prof. CHEN Qing-An from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed biomimetic prenylation and reverse-prenylation of indoles with isoprene. Their findings were published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed..
Recently, a research team led by Prof. CHEN Qing-An from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed biomimetic prenylation and reverse-prenylation of indoles with isoprene. Their findings were published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed..
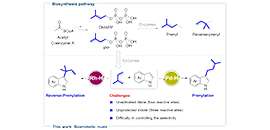
Biomimetic prenylation and reverse-prenylation of indoles with isoprene. (Image by HU Yan-Cheng)
Prenylation and reverse-prenylation are ubiquitous processes common to almost all living organisms. These reactions incorporate prenyl and reverse-prenyl moieties into various natural products with promising biological properties (e.g. indole alkaloids).
Nature employs dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) and isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) as starting materials for the biosynthesis of these molecules via enzyme catalysis. Besides, DMAPP and IPP are also precursors of isoprene emission in plants.
Intrigued by these biological processes, the researchers envisioned that isoprene may serve as a promising building block to install prenyl and reverse-prenyl groups on indoles via metal-hydride (M-H) catalysis.
This proposal was challenging, because the unbiased isoprene was difficult to form active metal π-allyl intermediate and the four alkenyl carbons of isoprene were electronically undifferentiated, resulting in six addition modes. Given indole also had three reactive sites (N, C2, C3), the reaction could theoretically generate 18 possible regioisomers.
Therefore, the selective formation of C3 reverse-prenylated and prenylated indoles was a daunting task. This goal was realized by the choice of M-H. Reverse-prenylated indoles were attained with high selectivity using Rh–H. By switching to a Pd–H catalyst, selectivity toward prenylated indoles was achieved.
The research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China and it is also one of the articles dedicated for the 70th anniversary of DICP. (Text by HU Yan-Cheng) -
 04 01, 2019Scientists Squeeze Catalysts inside Host Materials Like a Ship into a BottleScientists at Queen Mary University of London have found a way to place catalysts inside the tiniest pores of different host materials, a bit like when model ships are unfolded inside a bottle.
04 01, 2019Scientists Squeeze Catalysts inside Host Materials Like a Ship into a BottleScientists at Queen Mary University of London have found a way to place catalysts inside the tiniest pores of different host materials, a bit like when model ships are unfolded inside a bottle.
Scientists at Queen Mary University of London have found a way to place catalysts inside the tiniest pores of different host materials, a bit like when model ships are unfolded inside a bottle.
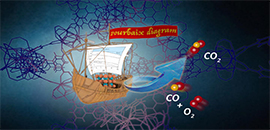
Using thermodynamic Pourbaix diagrams, scientists can squeeze catalysts inside host materials like a ship into a bottle. (Image by HOU Jingwei)
When materials are confined like this on such a small scale, and without breaking the host, they behave differently from their bulk form, a change that scientists call the confinement effect.
In the case of catalysts, which are materials that speed up chemical reactions, confinement may lead to higher activity. It keeps particles well separated, which is key to prevent loss of function in catalysis, and preserves their highly reactive surface.
Similarly, when a material is squeezed in a small space, its electrons are not free to move as far as usual and the material's light emission colour could change - an effect that could be used in micro lasers.
This strategy also opens up the possibility of multifunctional materials in which either the guest and host do different things separately or, because the guest is confined, the interactions between the host and guest may produce novel properties.
To illustrate the approach, the researchers used porous nanomaterials which are like sponges but with 1 nm pockets inside where other molecules can fit. However, loading reactive catalysts inside a nanoporous host is challenging because often the reaction conditions can destroy the host.
The study, published in Nature Communications, demonstrates a concept which uses thermodynamics to overcome these issues. The researchers realised that they can estimate the stability of the host under various reaction conditions.
The research was carried out with University of Cambridge, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (Chinese Academy of Sciences), National University of Singapore and The University of New South Wales.
Principal investigator Dr Stoyan Smoukov, from Queen Mary University of London, said: "We had some ideas that confinement could change properties, as such changes have been seen in other systems. The question was - was there a general way in which we could try and guide researchers so they could synthesise all kinds of large guests with various functions - like metals, metal oxides, sulfides, nitrides - without destroying the hosts?"
Using thermodynamic diagrams the researchers developed a concept called Pourbaix-Enabled Guest Synthesis (PEGS), where conditions and precursor compounds can be chosen not to destroy the hosts. They include a tutorial system that demonstrates how to make a large variety of new guest/host combination compounds.
Co-corresponding author, Professor Qiang Fu, from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (Chinese Academy of Sciences), added: "From a practical perspective, the PEGS approach links the materials chemistry with the design of functional materials for applications such as heterogeneous catalysis. The confined oxide nanostructures obtained by the PEGS method in this work can present enhanced catalytic performance, which is of great significance for design of advanced oxide catalysts."
One of the lead authors, Tiesheng Wang, from the University of Cambridge, said: "The upcoming impact can be enormous. Since quantum theory describes nature at atomic-to-subatomic scales, the work that helps to achieve new confined states at small scales may contribute to the foundation to explore the quantum world experimentally." (By Eurek!Alert) -
 04 01, 2019Scientists Review Single-Atom Catalysis for Carbon Dioxide Transformation
04 01, 2019Scientists Review Single-Atom Catalysis for Carbon Dioxide Transformation
Recently, a research group led by Prof. HUANG Yanqiang and Prof. ZHANG Tao from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported an advanced review paper entitled "Single-Atom Catalysis toward Efficient CO2 Conversion to CO and Formate Products" in Account of Chemical Research. It briefly summarized the newly research on the development of single-atom catalysts for efficient catalytic conversion of CO2 and it was selected as the supplementary cover article.
Single-atom catalysts offer great opportunity for efficient conversions of CO2 with well-defined sites from metal individuals and the collaboration with substrate microenvironments. (Image by SU Xiong)
The concept of “Single-Atom Catalysis” was jointly proposed by Prof. ZHANG Tao from DICP, Prof. LI Jun from Tsinghua University, and Prof. LIU Jingyue from Arizona State University in 2011. In recent years, lots of research groups have made outstanding progress in the fields of electrocatalysis, photocatalysis and traditional heterogeneous catalysis based on single-atom catalysis. The review focuses on the efficient catalytic conversion of CO2 by single-atom catalysts.
Prof. HUANG Yanqiang and colleagues have long been committed to the research of thermo- and electric- catalytic conversion of CO2. By means of the utilization of lattice-matching strategy between metal and support, the functionalization of carrier with additive groups and the regulation of the electronic state of active centers and so on, the product selectivities for CO2 transformation were controllable. The particularity of the specific structure of single-atom catalyst provided an ideal model for the activation and directional transformation of CO2.
By utilizing the characteristics of lattice matching of the same crystal type between IrO2 and rutile TiO2, a highly thermal-stable Ir1/TiO2 catalyst was prepared, which was demonstrated to be efficient in selective transformation of CO2 to CO (ACS Catalysis).
In collaboration with Prof. LIU Bin' team from Nanyang Technological University, a nitrogen-doped graphene anchored Ni single-atom catalyst was developed. With the facility of the unpaired 3d electrons in the outermost layer of Ni single atom easily to be delocalized and the formation of electronegative Ni-CO2δ- species, a highly efficient electrochemical reduction process of CO2 to CO was realized (Nature Energy).
By simulating the efficient transforming mechanism of CO2 over homogeneous catalyst at low temperature, a single-atom Ir catalyst supported by a porous organic polymer carrier containing pyridine-amide groups was fabricated. On this basis, the quasi-homogeneous activation and catalytic conversion of CO2 were successfully achieved (Nature Communications; Chem).
These results provided new ideas for the design of high efficiency CO2 reduction catalysts.
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the CAS, and etc. This is also one of the articles dedicated for the 70th anniversary of DICP. (Text by SU Xiong) -
 03 26, 2019DICP Scientists Investigate Aerobic Oxidative Cleavage of 1,2-DiolsRecently, Dr. WANG Lianyue and Prof. GAO Shuang at the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported aerobic oxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols and insights into the reaction pathway. Their findings were published in Communications Chemistry.
03 26, 2019DICP Scientists Investigate Aerobic Oxidative Cleavage of 1,2-DiolsRecently, Dr. WANG Lianyue and Prof. GAO Shuang at the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported aerobic oxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols and insights into the reaction pathway. Their findings were published in Communications Chemistry.
Recently, Dr. WANG Lianyue and Prof. GAO Shuang at the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported aerobic oxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols and insights into the reaction pathway. Their findings were published in Communications Chemistry.
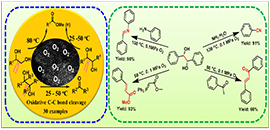
Aerobic oxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols catalyzed by atomic-scale cobalt and its application in tandem reactions (Image by WANG Lianyue)
The oxidative cleavage of the C-C bonds in 1,2-diols to the corresponding carbonyl compounds is one of the most important transformation in synthetic organic chemistry. The classical methods for cleaving the C-C bond of 1,2-diols use stoichiometric or excess amount oxidants, such as periodic acid and its salts or lead tetraacetate.
Up to now, these methods remain the most widely used for vicinal diols cleavage. But these oxidants produce equimolar quantities of toxic waste and cannot meet the current environmental sustainable development needs. Therefore, the development of catalytic oxidation processes with a clean oxidant such as molecular oxygen is an alternative and promising protocol.
Although the early homogeneous transition-metal catalytic systems are capable of cleaving simple diols with molecular oxygen, most of them are still suffering from drawbacks such as low product selectivity, limited substrate range, the use of expensive noble metals (e.g., Pd, Ru), the required harsh conditions, and no reusability of the catalyst.
Therefore, development of a sustainable and cost efficient heterogeneous catalysts to achieve oxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols to synthesize carbonyl compounds under mild and green conditions has become an important consideration for the design of catalysts.
Scientists reported a Co-based heterogeneous catalyst supported on nitrogen-doped carbon materials with improved catalytic performance in the aerobic oxidative cleavage of a variety of 1,2-diols into esters, aldehydes or ketones under mild conditions with O2 or air as the oxidant. For example, the oxidative cleavage of pinacol was achieved at ambient temperature and air pressure. It was also effective for the application of oxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols in tandem reactions.
Based on a large number of control experiments, kinetics and isotope labeling experiments, the oxidative cleavage processes of terminal diols and pinacol were studied respectively. Mechanistic insights into the cleavage of terminal diols revealed that a sequence reaction, involving stepwise oxidation/nucleophilic addition /C-C bond cleavage was disclosed. Mechanistic investigations on pinacol give a conclusion that trans isomer, meso-hydrobenzoin was fast cleaved faster than the cis isomer, (S,S)-hydrobenzoin and that the reaction followed a type II mechanism via the formation of a monodentate complex between diol and active oxidant species, which then oxidatively collapses to the carbonyl product in a two-electron oxidation.
Moreover, mild reaction conditions, non-noble metal catalyst and excellent reusability of the catalyst made the present catalytic system more competitive than the existing ones.
This study will provide a new idea for the development of catalysts for oxidative cleavage of C-C bonds.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Major Science and Technology Innovation Project. (Text by WANG Lianyue) -
03 22, 2019Plant Scraps are the Key Ingredient in Cheap, Sustainable Jet FuelScientists in China have developed a process for converting plant waste from agriculture and timber harvesting into high-density aviation fuel. Their research, published March 21 in the journal Joule, may help reduce CO2 emissions from airplanes and rockets.
Scientists in China have developed a process for converting plant waste from agriculture and timber harvesting into high-density aviation fuel. Their research, published March 21 in the journal Joule, may help reduce CO2 emissions from airplanes and rockets.
Cellulose, one of the main components of agriculture waste and forest residue, is a cheap, renewable, and highly abundant polymer that forms the cell walls of plants. While chain alkanes (such as branched octane, dodecane, and hexadecane) have previously been derived from cellulose for use in jet fuel, the researchers believe this is the first study to produce more complex polycycloalkane compounds that can be used as high-density aviation fuel.
Ning Li, a research scientist at the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and an author of the study, believes this new biofuel could be instrumental in helping aviation "go green."
"Our biofuel is important for mitigating CO2 emissions because it is derived from biomass and it has higher density (or volumetric heat values) compared with conventional aviation fuels," says Li. "As we know, the utilization of high-density aviation fuel can significantly increase the range and payload of aircraft without changing the volume of oil in the tank."
To produce this biofuel, Li and his team found that cellulose can be selectively converted to 2,5-hexanedione using the chemical reaction hydrogenolysis. They then developed a method of separating the compound 2,5-hexanedione by converting the 5-methylfurfural in hydrogenolysis product to 2,5-hexanedione, while keeping 2,5-hexanedione in the product unchanged. This resulted in a 71% isolated carbon yield--a 5% increase from the product yield in their initial work. Finally, they reacted hydrogen with the 2,5-hexanedione from wheatgrass cellulose to obtain the final product: a mixture of C12 and C18 polycycloalkanes with a low freezing point and a density about 10% higher than that of conventional jet fuels. Much of the biofuel's magic lies in this high density--it can be used as either a wholesale replacement fuel or as an additive to improve the efficiency of other jet fuels.
"The aircraft using this fuel can fly farther and carry more than those using conventional jet fuel, which can decrease the flight number and decrease the CO2 emissions during the taking off (or launching) and landing," says Li.
Although the researchers produced the biofuel at a laboratory scale in this study, Li and his team believe the process' cheap, abundant cellulose feedstock, fewer production steps, and lower energy cost and consumption mean it will soon be ready for commercial use. They also predict it will yield higher profits than conventional aviation fuel production because it requires lower costs to produce a higher-density fuel. The biggest issue holding the process back is its use of dichloromethane to break down cellulose into 2,5-hexanedione; the compound is traditionally used as a solvent in paint removers and is considered an environmental and health hazard.
"In the future, we will go on to explore the environmentally friendly and renewable organic solvent that can replace the dichloromethane used in the hydrogenolysis of cellulose to 2,5-hexanedione," says Li. "At the same time, we will study the application of 2,5-hexanedione in the synthesis of other fuels and value-added chemicals." (By EurekAlert!)