Research News
-
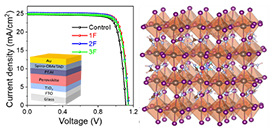 07 30, 2021Fluoroethylamine Engineering for Effective Passivation Improves Efficiency of Perovskite Solar CellsResearchers incorporated fluoroethylamine (FEA) cations into perovskite films to form highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells (PSCs) with a high-power conversion efficiency of 23.4%.
07 30, 2021Fluoroethylamine Engineering for Effective Passivation Improves Efficiency of Perovskite Solar CellsResearchers incorporated fluoroethylamine (FEA) cations into perovskite films to form highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells (PSCs) with a high-power conversion efficiency of 23.4%.
Perovskite film, a key layer of the perovskite solar cell (PSC), determines the performance and stability of the device.
In the preparation process of PSCs, many defects will inevitably be introduced at the grain boundaries and interfaces, which will act as non-radiative recombination centers and seriously damage the performance and stability of PSCs.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. LIU Shengzhong from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and his cooperators incorporated fluoroethylamine (FEA) cations into the perovskite film to form highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells (PSCs).
This study was published in Advanced Energy Materials on June 23.
The researchers found that perovskite film with FEA passivation improved photoluminescence (PL) intensity, prolonged carrier-lifetime, suppressed nonradiative recombination, enlarged grain size and hydrophobicity, and hence delivered high device performances.
By engineering of different amounts of fluorine in the molecule, they revealed that different amounts of fluorine additives presented a gradient distribution in the film. The device employing 2-fluoroethylamine (1FEA) achieved an efficiency of 23.40%, while the device employing 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethylamine (3FEA) showed the best environmental stability, maintaining 87% of their initial efficiencies after 1200 h.
"This research paves a new way to fabricate high-efficiency and stabile PSCs," said Prof. LIU.
The above work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the DNL Cooperation Fund CAS, the 111 Project, and the Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team. (Text by SU Hang and DUAN Lianjie) -
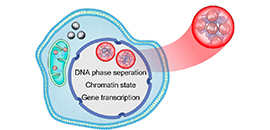 07 30, 2021Researchers Reveal Molecular Mechanism of Ruthenium Complex Induced DNA Phase SeparationResearchers revealed the molecular mechanism of ruthenium complex induced DNA phase separation in living cells.
07 30, 2021Researchers Reveal Molecular Mechanism of Ruthenium Complex Induced DNA Phase SeparationResearchers revealed the molecular mechanism of ruthenium complex induced DNA phase separation in living cells.
The phenomenon of "liquid-liquid" phase separation (LLPS) of biological macromolecules in living cells regulates many cell activities.
DNA LLPS manipulates many important processes such as gene transcription, translation, and chromosome high-level structure assembly. Abnormal of DNA LLPS causes oncogene expression, genome inactivation, uncontrolled transcription activation and other cellular processes, which are directly related to fatal diseases.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. LI Guohui from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. MAO Zongwan's group from Sun Yat-Sen University, revealed the molecular mechanism of ruthenium complex induced DNA phase separation in living cells.
This study was published in Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 22.
Illustration of the mechanisms of DNA phase separation induced by ruthenium complex (Image by ZHANG Yuebin and LI Guohui)
Prof.Mao' group proposed a metal ruthenium complex with high DNA affinity and photo-switching properties to fulfill the real-time detecting and monitoring of DNA phase separation process in living cells. In addition, the metal ruthenium complexes also exhibited potent anticancer activity both in Vitro and in Vivo conditions.
Prof LI’s group utilized multi-scale molecular dynamics simulations to unveil the underlying mechanism of ruthenium complex induced DNA phase separation, where the positively charged lipophilic triphenylphosphine substituents and the flexible long alkyl chains of the ruthenium complex provided significant contributions in inducing DNA assembly.
This study provides new ideas for the design of interventional reagents for inducing DNA phase separation of living cells.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. (Text by ZHANG Yuebin and LI Guohui) -
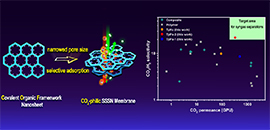 07 29, 2021Single-Phase Covalent Organic Frameworks Membranes Make CO2-selective Separation PossibleScientists developed a novel strategy for the fabrication of single-phase CO2-selective covalent organic frameworks (COFs) nanosheet membranes with both high CO2/H2 separation factors and high CO2 permeances for the very first time. These membranes reached the target with commercial feasibility for syngas separations.A research group led by Prof. YANG Weishen and Dr. PENG Yuan from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed a novel strategy to fabricate single-phase CO2-selective covalent organic frameworks (COFs) nanosheet membranes featured with both high CO2/H2 separation factors and high CO2 permeances.This study was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition on July 20.Two-dimensional (2D) COFs, a class of crystalline organic skeletons possessing permanent one-dimensional pores, are promising to serve as high-quality membrane materials in CO2 capture field. However, their inherent pore sizes (>0.8 nm) are too large to provide desired molecular sieve capability for gas separations currently.Illustration of superior CO2-selective COF nanosheet membrane for high-performance CO2/H2 separation (Image by PENG Yuan)The researchers exfoliated three kinds of 2D COFs, that is, TpPa-1, TpPa-2 and TpHz (Tp=1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol, Pa-1=benzene-1,4-diamine, Pa-2=2,5-dimethylbenzene-1,4-diamine, Hz=hydrazine), with an average particle size of 3 um and different pore sizes into 2 nm-thick nanosheets. Intact crystallinities and functionalities were well-retained after exfoliation treatment.They found that even the TpHz with relatively smallest inherent pore size could not exhibit desired gas separation performance in a form of conventional bulk membrane. With ultrathin nanosheets served as membrane building units, they developed novel COF nanosheet membranes exhibiting distinctive staggered stacking micro-structures."Just like the fishing net, you can irregularly pile up several nets to catch tiny fish" said Dr. PENG.The intriguing membrane structures in collaboration with inherent CO2-selective adsorption capacities of COF frameworks endowed the COF nanosheet membranes with permeation priority of large CO2 molecules from mixed CO2/H2 gas based on a surface diffusion mechanism.Among the membranes, TpPa-2 nanosheet membranes with medium pore size showed the highest CO2/H2 separation factor and CO2 permeance, which reached the target with commercial feasibility for syngas separations.The researchers identified that the TpPa-2 nanosheet membranes exhibited proper narrowed pores derived from the staggered stacking patterns, which allowed exactly two columns of CO2 molecules to pass through and maximized the blocking effect for H2 passage.This study provides a new pore engineering strategy for the design and manufacture of high-performance COF membranes in gas separation realm."Taking full advantage of this pore-engineering strategy, different categories of COFs with diversified pore structures can enable specified membrane-based gas separations," said Prof. Yang.This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the DNL Cooperation Fund, and the DICP Fund. (Text by PENG Yuan)
07 29, 2021Single-Phase Covalent Organic Frameworks Membranes Make CO2-selective Separation PossibleScientists developed a novel strategy for the fabrication of single-phase CO2-selective covalent organic frameworks (COFs) nanosheet membranes with both high CO2/H2 separation factors and high CO2 permeances for the very first time. These membranes reached the target with commercial feasibility for syngas separations.A research group led by Prof. YANG Weishen and Dr. PENG Yuan from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed a novel strategy to fabricate single-phase CO2-selective covalent organic frameworks (COFs) nanosheet membranes featured with both high CO2/H2 separation factors and high CO2 permeances.This study was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition on July 20.Two-dimensional (2D) COFs, a class of crystalline organic skeletons possessing permanent one-dimensional pores, are promising to serve as high-quality membrane materials in CO2 capture field. However, their inherent pore sizes (>0.8 nm) are too large to provide desired molecular sieve capability for gas separations currently.Illustration of superior CO2-selective COF nanosheet membrane for high-performance CO2/H2 separation (Image by PENG Yuan)The researchers exfoliated three kinds of 2D COFs, that is, TpPa-1, TpPa-2 and TpHz (Tp=1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol, Pa-1=benzene-1,4-diamine, Pa-2=2,5-dimethylbenzene-1,4-diamine, Hz=hydrazine), with an average particle size of 3 um and different pore sizes into 2 nm-thick nanosheets. Intact crystallinities and functionalities were well-retained after exfoliation treatment.They found that even the TpHz with relatively smallest inherent pore size could not exhibit desired gas separation performance in a form of conventional bulk membrane. With ultrathin nanosheets served as membrane building units, they developed novel COF nanosheet membranes exhibiting distinctive staggered stacking micro-structures."Just like the fishing net, you can irregularly pile up several nets to catch tiny fish" said Dr. PENG.The intriguing membrane structures in collaboration with inherent CO2-selective adsorption capacities of COF frameworks endowed the COF nanosheet membranes with permeation priority of large CO2 molecules from mixed CO2/H2 gas based on a surface diffusion mechanism.Among the membranes, TpPa-2 nanosheet membranes with medium pore size showed the highest CO2/H2 separation factor and CO2 permeance, which reached the target with commercial feasibility for syngas separations.The researchers identified that the TpPa-2 nanosheet membranes exhibited proper narrowed pores derived from the staggered stacking patterns, which allowed exactly two columns of CO2 molecules to pass through and maximized the blocking effect for H2 passage.This study provides a new pore engineering strategy for the design and manufacture of high-performance COF membranes in gas separation realm."Taking full advantage of this pore-engineering strategy, different categories of COFs with diversified pore structures can enable specified membrane-based gas separations," said Prof. Yang.This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the DNL Cooperation Fund, and the DICP Fund. (Text by PENG Yuan) -
 07 28, 2021Oxygen-vacancy-mediated Catalysis Boosts Direct Methanation of BiomassScientists proposed interfacial oxygen-vacancy (Vo)-mediated catalysis over Ru/TiO2 for the direct methanation of lignocellulosic biomass at temperatures below 200 °C and with a selectivity above 95%.
07 28, 2021Oxygen-vacancy-mediated Catalysis Boosts Direct Methanation of BiomassScientists proposed interfacial oxygen-vacancy (Vo)-mediated catalysis over Ru/TiO2 for the direct methanation of lignocellulosic biomass at temperatures below 200 °C and with a selectivity above 95%.
Biomethane (CH4) can be used as feedstock for modern chemical industry or burned directly as a fuel.
Currently, CH4 is mainly produced via a multi-step process in which biomass is first gasified into biogas, followed by the methanation of the latter. This method requires high temperature and pressure and shows low selectivity for chemical or biological processes.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WANG Feng from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. WANG Min's group from Dalian University of Technology, proposed interfacial oxygen-vacancy (Vo)-mediated catalysis over Ru/TiO2 for the direct methanation of lignocellulosic biomass at temperatures below 200 °C and with a selectivity above 95%.
The results were published in Joule on July 27.
"We proposed the Vo-mediated catalysis process to couple the oxidation of biomass into CO2 with the hydrogenation of CO2 into CH4, leading to the direct methanation of biomass under mild conditions," said Prof. WANG Min.
The researchers found that the biomass substrate molecule was oxidized by the lattice oxygen of Ru/P25 into CO2, and Vo formed on Ru/P25. Subsequently, the dissociated oxygen atoms derived from CO2 could restore the Vo during the CO2 hydrogenation process.
Moreover, they found that the Vo-mediated catalysis process could stably catalyze the production of CH4 from aqueous glycerol at temperatures as low as 120 °C and with a selectivity above 99%.
"This direct methanation process is simpler and more efficient than the traditional two-step process of biogas production and methanation," said Prof. WANG Feng. "It opens up a new route for the utilization of biomass resources."
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China, and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. (Text by ZHOU Ruhong) -
 07 27, 2021Scientists Unveil Potential Dependence in Nitric Oxide Electroreduction to AmmoniaScientists unveiled the potential dependence of products selectivity in electrochemical NO reduction (eNORR) to ammonia.
07 27, 2021Scientists Unveil Potential Dependence in Nitric Oxide Electroreduction to AmmoniaScientists unveiled the potential dependence of products selectivity in electrochemical NO reduction (eNORR) to ammonia.
Nitrogen oxide (NOx), such as nitric oxide (NO), are environmental pollutants. They are often removed via selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology.
A novel artificial nitrogen cycle path driven by electrocatalysis has been proposed to couple conventional denitrification and ammonia (NH3) synthesis. However, further studied showed that direct electroreduction of NOx to N2 was difficult in any potential.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. XIAO Jianping from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences unveiled the potential dependence of products selectivity in electrochemical NO reduction (eNORR) to ammonia.
This study was published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters on July 20.
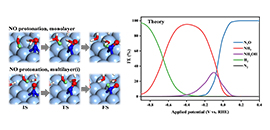
(a)-(b) Verification of monolayer water model in electrocatalytic energy barrier calculations; (c)-(d) Comparison of theoretical and experimental Faradaic efficiency (Image by LONG Jun)
The researchers took Ag as model catalyst. They verified the reliability of monolayer water model in electrocatalytic energy barrier calculations and obtained the energetics of NORR network by density functional theory calculations. Finally, they developed a microkinetic model to rationalize the general selectivity trend of eNORR with varying potential.
This model reproduced the experimental Faradaic efficiency well, quantitatively describing the selectivity turnover from N2O to NH3 and from NH3 to H2 as applies more negative potential.
The first turnover of selectivity was due to the thermochemical coupling of two NO* limiting the N2O production. The second turnover was attributed to the more significant potential-dependence of HER than NH3 production.
"This model provides a theoretical guide for the design of selective electrocatalytic of NOx, which is also beneficial to understand the potential dependence of some other electrocatalytic reduction reactions," said Prof. XIAO.
The above work was supported by the DNL Cooperation Fund of CAS, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS. (Text by LONG Jun) -
 07 26, 2021Dalian Coherent Light Source Reveals Strong Isotope Effects in Photodissociation of Water Isotopologue
07 26, 2021Dalian Coherent Light Source Reveals Strong Isotope Effects in Photodissociation of Water Isotopologue
Recently, a research group led by Prof. YUAN Kaijun and Prof. YANG Xueming from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed strong isotope effects in the photodissociation of the water isotopologue (HOD) using the Dalian Coherent Light Source.
Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 21.
Dalian Coherent Light Source revealing strong isotope effects in water photochemistry (Image by YUAN Kaijun)
"Our experimental results illustrate dramatically different quantum state population distributions of OH and OD fragments from HOD photodissociation. The branching ratios of the H+OD and D+OH channels display large wavelength-dependent isotopic fractionation," said Prof. YUAN.
Because water is the most abundant species in the solar nebula, photodissociation of water and its isotopologue by solar vacuum ultraviolet photons may be an alternative source of the D/H isotope heterogeneity, and this effect must be considered in photochemical models.
The photochemical processes identified in this work may vary the D/H isotopic ratios in the inner and outer regions, and/or in different periods of the solar nebula, which cause the D/H isotope heterogeneity in the solar system.
This research was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chemical Dynamics Research Center, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. (Text by YUAN Kaijun)