Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) due to the abundant sodium resources, suitable redox potential, and similar charge store mechanism.
However, the larger diameter of Na ions compared to Li ions makes the sodiation/desodiation process more difficult with a larger volumetric variation of the electrode material, thus leading to poor capacity and cycling stability. Therefore, a rational design of electrode materials is critical for improving the electrochemical performance of SIBs.
A research group led by Prof. DENG Dehui from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. ZHANG Jianan from Zhengzhou University, reported a synergetic effect of atomic-interface from well-constructed 2H-MoS2/Fe(SA)-N-C anode assembled with 2H-MoS2 layer on N-doped carbon confined Fe atom, which boosts the reversible sodium storage capacity.
This study was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition on Feb.2.
Regulating the catalytic process by atomic-interface for enhanced sodium ion storage (Image by XIA Huicong and ZAN Lingxing)
The researchers found that driven by the work function difference at the heterointerface, the electron could transfer from Fe(SA)-N-C to 2H-MoS2 easily, enhancing the adsorption Na+ ion at the S sites of electron-rich MoS2.
Meanwhile, they also indicated that the spin-state of Fe site of Fe(SA)-N-C optimized the electronic structure and catalytic activity of the Fe site.
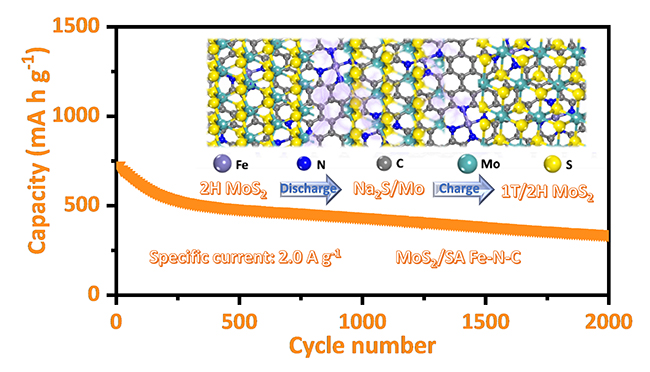
Compared with nitrogen-doped carbon (N-C) and pure carbon, the Fe sites of Fe(SA)-N-C could effectively promote the phase transition and structural evolution of 1T/2H-MoS2 during the sodiation/desodiation process, thus prolonging the lifetime of the materials. The 2H-MoS2/Fe(SA)-N-C anode showed a robust long-term cycling performance with a capacity of 350 mA h g-1 after 2000 cycles at 2.0 A g-1.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS, and the Danish company Haldor Topsoe A/S.