Gasoline, the primary transportation fuel, contains hydrocarbons with 5-11 carbons (C5-11) and is almost derived from petroleum at present.
Gasoline can also be produced from non-petroleum syngas. Nonetheless, achieving high conversions of syngas to C5-11 with excellent selectivity and stability remains a challenge.
A research group led by Prof. LIU Zhongmin and Prof. ZHU Wenliang from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences realized highly efficient and selective conversion of syngas to gasoline-range liquid hydrocarbons over a dual-bed catalyst.
The study was published in Chem Catalysis on April 2.
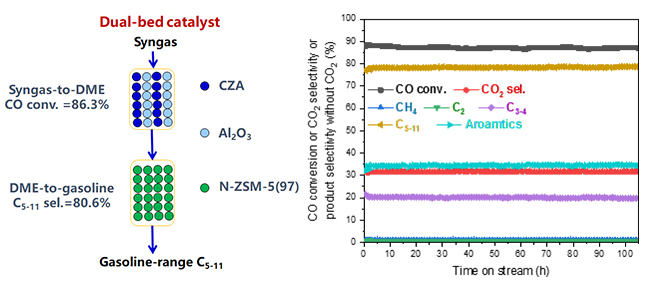
Schematic diagram for the conversion of syngas to gasoline-range liquid hydrocarbons over a dual-bed catalyst (CZA+Al2O3)/N-ZSM-5(97) and results of the stability test (Image by NI Youming)
This dual-bed catalyst, (CZA +Al2O3)/N-ZSM-5(97), consists of the conventional syngas-to-dimethyl ether catalyst CZA + Al2O3 in the upper bed and a dimethyl ether-to-gasoline catalyst N-ZSM-5(97) in the lower bed.
The selectivity of C5-11 and C3-11 in the hydrocarbon products reached 80.6% and 98.2%, respectively, along with 86.3% CO conversion.
The catalyst exhibited excellent stability, and the iso/n-paraffin ratio in the C5-11 products was up to 18. The nano-sized structure of N-ZSM-5(97) was beneficial for reducing coke and prolonging the lifetime; meanwhile, the low acid content of N-ZSM-5(97) was advantageous for increasing the C5-11 selectivity.
Compared with the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis process, this dual-bed syngas-to-gasoline (STG) process was more suitable for producing high-quality gasoline, along with the co-production of aromatic hydrocarbons.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. (Text by NI Youming)