All-inorganic zero-dimensional (0D) metal halides are widely applied in the fields of display and solid-state lighting due to their excellent photoluminescence (PL) properties and high stability.
At present, 0D metal halides have achieved high photoluminescence quantum yields (PLQYs) in green, yellow and red light region. By contrast, the development of high-efficiency blue-emitting 0D metal halides remains challenging.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. HAN Keli from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences studied the dynamic mechanism of all-inorganic 0D metal halides, and obtained high PLQY in pure-blue spectral region by doping copper into cesium zinc halides.
This work was published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. on August 12.
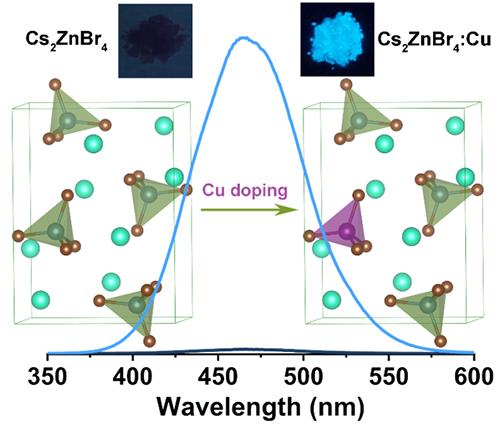
The doping of Cu+ into 0D Cs2ZnBr4 caused an evident excitonic absorption peak, and successfully transformed the weakly luminescent Cs2ZnBr4 to a bright blue-emitting material with high PLQY. (Image by CHENG Pengfei)
The scientists synthesized copper doped 0D cesium zinc halide single crystals. After the incorporation of Cu+ into Cs2ZnBr4, an obvious exciton absorption peak appeared, while the PL peak position did not change.
The PLQY increased from 3.6% to 65.3%. Meanwhile, the PL lifetime was significantly longer, indicating that Cu+ doping could effectively inhibit the non-radiative recombination process in Cs2ZnBr4.
Detailed spectral analysis showed that the blue emission in Cs2ZnBr4:Cu originated from triplet self-trapped excitons, and exhibited the characteristics of dual emission at low temperatures. And Cs2ZnBr4:Cu also exhibited good humidity and thermal stability.
In addition, scientists obtained an efficient sky-blue emission (PLQY ~73.1%) of Rb2ZnCl4:Cu by substitution a-site cation and halogen.
This work provides an effective strategy for the development of environmentally friendly, low-cost and high-efficiency blue-emitting 0D all-inorganic metal halides.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National Key Research and Development Program of China. (Text by CHENG Pengfei)