Enzyme biosensor is a miniaturized instrument for quantitative determination of target by capturing the signal generated by the reaction between target and enzyme.
Enzyme is highly sensitive to external environment such as temperature, solvent, pH value, and its shelf life is very short, limiting the application of enzyme biosensor.
Recently, Prof. LU Xianbo and Prof. CHEN Jiping from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences armored the enzyme with single molecule enzyme nanocapsules (SMENs) in enzyme biosensor, which effectively improved the thermal stability, organic solvent tolerance, acid-base tolerance, and storage and usage stability of enzyme biosensor.
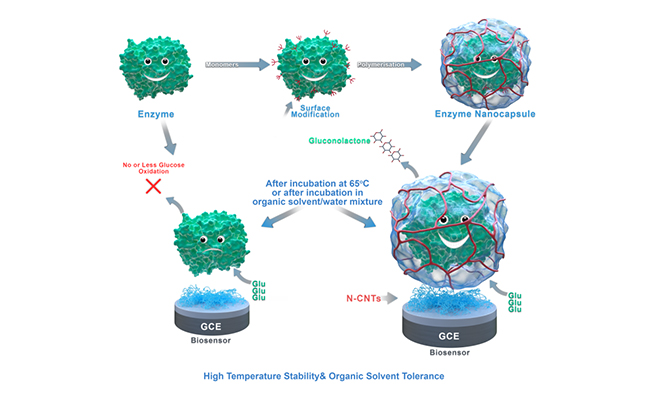
Schematic illustration of preparation, application and improved stability of SMENs based biosensor for glucose detection (Image by LU Xianbo)
SMENs technology is a method to wrap the enzyme molecule with a polymer shell, forming a capsule structure. The porous structure of the polymer shell can ensure the reaction between the enzyme and the outside target and maintain the activity of the enzyme at the same time. Moreover, the polymer shell can protect the enzyme molecule from the external environment and improve the stability of enzyme.
To verify the stability of enzyme biosensors using nanocapsule technology, the scientists chose glucose oxidase and tyrosinase as model enzymes.
They found that the polymer shell could stabilize the internal glucose oxidase and tyrosinase core, while the porous structure could realize the rapid transport of the target, thus forming a new class of biocatalytic nanocapsules with high activity and stability.
The novel nanocapsule enhanced the stability of the encapsulated enzyme molecule, provided a biocompatible microenvironment, avoided structural denaturation under conditions such as high temperature, strong acid and base, and helped to retain the water molecules necessary for enzyme activity during the operation in the organic solvent system.
The biosensors based on glucose oxidase nanocapsules and tyrosinase nanocapsules showed good performance in blood glucose detection and bisphenol A detection respectively.
The SMENs-based biosensor has potential applications in the fields of analysis, biomedical detection, wearable devices, and implantable devices.
The results were published in Biosensors & Bioelectronics and Analytical Chemistry.
The above work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Innovation Research Dund of of DICP, CAS. (Text by LU Xianbo, WU Lingxia, and Dhanjai)