Recently, a research group led by Prof. CHEN Qing'an from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed an asymmetric three-component coupling strategy for the rapid synthesis of chiral α-quaternary amino acids. This study was published in Cell Reports Physical Science on May 27.
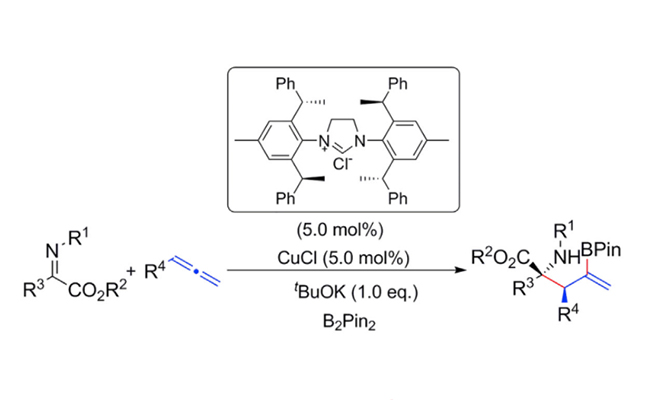
Copper-Catalyzed Asymmetric Synthesis α-Quaternary Amino Esters. (Image by ZHAO Chaoyang and HU Yancheng)
Optically active α-quaternary amino acids (AAs) play an important role in the synthesis of unnatural peptides and proteins with specific biological activities. Besides, they are also prevalent in a variety of bioactive natural products.
However, exploiting a catalytic asymmetric strategy to access chiral α-quaternary amino acids remains challenging due to the rigorous requirement in simultaneous control of the chemo-, regio-, diastereo- and enantio-selectivity.
The researchers from DICP developed a copper-catalyzed enantioselective three-component coupling of allenes, diboron, and ketiminoesters for the synthesis of chiral quaternary amino esters with adjacent stereocenters. The high stereochemical control was enabled by employing bulky C2-symmetric N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) as chiral ligand.
This protocol also features mild reaction conditions, wide substrate scope, and diverse applications in organic synthesis.
In addition, the researchers conducted density functional theory (DFT) calculations to better understand why chiral C2-symmetric NHC ligand is superior in the control of the diastereo- and enantio-selectivity of the reaction. (Text by ZHAO Chaoyang and HU Yancheng)