X-ray detectors are widely used in medical diagnosis, environmental monitoring, safety inspection. In recent years, the organic-inorganic lead halide perovskites with low cost and facile preparation process have shown excellent properties in direct X-ray detection. However, the issues raised by the toxic lead element and marginal stability due to the volatile organic components have limited their potential applications.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. LIU Shengzhong (Frank) from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a lead-free perovskite Cs3Bi2I9 single-crystals for high-performance X-ray detection.
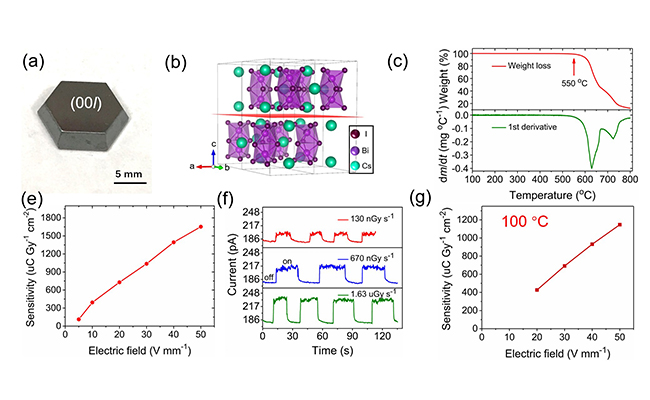
They developed a nucleation-controlled solution method to grow large-size high-quality Cs3Bi2I9 perovskite single crystals (PSCs). Using the technique, they could harvest some centimeter-sized single crystals and achieved high device performance.
The X-ray detectors based on the Cs3Bi2I9 single crystals exhibited high sensitivity and very low detectable dose rate, both are desired in medical diagnostics.
In addition, the X-ray detectors showed high X-ray imaging capability due to its negligible signal drifting and extremely high stability.
Furthermore, the outstanding thermal stability of the Cs3Bi2I9 PSCs were inspired to develop a high temperature X-ray detector with stable response at up to 100°C.
The Cs3Bi2I9 perovskite single crystal based X-ray detector. (Image by DUAN Lianjie and ZHANG Yunxia)
Their findings were published in Nature Communications. (Text by DUAN Lianjie and ZHANG Yunxia)