A research team led by HAN Keli from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences synthesized undoped and Sb-doped lead-free zero-dimensional (0D) perovskites. Doping Sb3+ ions achieved a significant boost of the photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) from less than 2% to 85-95%.
They further investigated the stability and dynamics mechanism. Their findings were published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed..
All-inorganic lead-free 0D perovskites have drawn wide attention due to non-toxicity, unique structures and optoelectronic properties.
Previous studies have focused on the stability of all-inorganic lead-free 0D perovskite, but the PLQY is still very low compared to organic-inorganic hybrid 0D perovskite. Therefore, it's needed to develop highly efficient and stable all-inorganic lead-free 0D perovskite and clarify its dynamics mechanism.
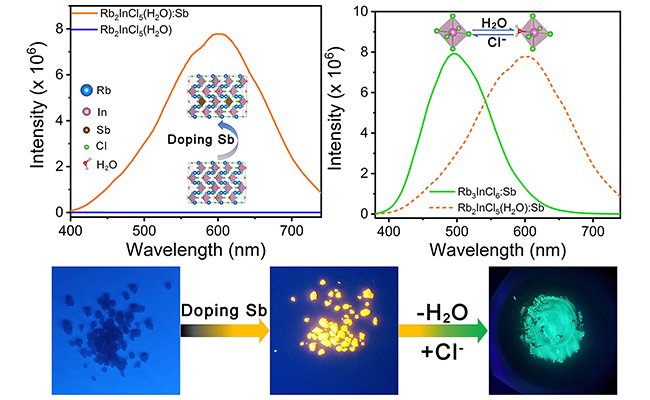
PL spectra and photographs under UV light of the 0D In-based perovskites. (Image by HAN Peigeng, LUO Cheng)
The scientists synthesized Sb-doped lead-free direct bandgap In-based 0D perovskites A2InCl5(H2O):Sb (A = Rb, Cs), which showed enhanced yellow photoluminescence (PL) emission. To study the effect of coordination H2O, A3InCl6:Sb (A = Rb, Cs) were also synthesized and showed bright green emission.
They further explored the effect of Sb3+ dopants and the origin of bright emission by ultrafast transient absorption techniques. In addition, Sb-doped 0D rubidium indium chloride perovskites exhibited excellent stability.
Their findings not only provided a way to design a set of new high-performance 0D lead-free perovskites, but also revealed the relationship between structure and PL properties.
This study was supported by the key research project of National Natural Science Foundation. (Text by HAN Peigeng)