Cell components consist of functional biological macromolecules, including proteins and nucleic acids, as well as their environment and function modulator small molecules, including organic molecules, phospholipids, water and metal ions. Identification of proteins and small molecules, proteins and the complex itself and the interaction between the two are the two primitive processes in the functionality of cells. Our biomolecular simulation study group (1106), since its inception in 2009, has been devoted to the development of theoretical approaches and applying these techniques to study these primitive processes.
Identification and interaction between drug molecule and its targeted protein molecule is one of the primitive processes as described above. By understanding the molecular mechanisms of the occurrence and transformation of diseases, new drug development costs and cycles are increasingly beyond people's expectations. Since the unpredictability in preliminary studies of marketed drugs as well as the complexity of human body and the disease itself, they become the drug of choice to treat some diseases. Discovering new uses in drug already on the market has become a hot and difficult research target.
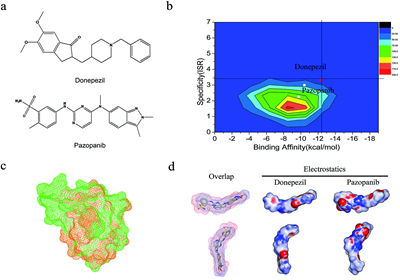
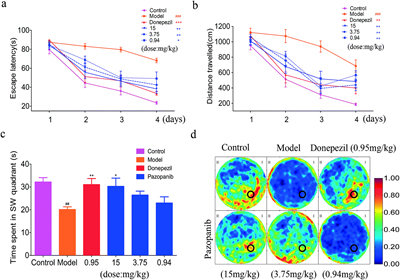
Based on years of experience in cooperation with international biopharmaceutical companies as well as the experience in molecular modeling and theoretical method development, our group, in collaboration with Professor Yang Yongliang Dalian University of Technology, proposed a new calculation method. Taking advantage of the geometrical and biochemical similarities of drug molecules and protein binding pockets, molecular dynamics simulation calculations may be used to determine marketed drugs with similar functionalities. Specifically for the existed drug donepezil dealing with Alzheimer's disease (Alzhmeir Disease / AD), calculated using the newly developed strategy, found a kidney cancer drug pazopanib may have with a similar function. The effect of pazopanib was further proved by experiments in protein level as well as organism level, with only 1/5 dose of donepezil was needed thus the toxicity was also greatly reduced. Our research expanded the use of existing drugs, and provided a new research strategy to locate new features of existing drugs. The paper published on文章发表在Chemical Science 2015 "Computational discovery and experimental verification of tyrosine kinase inhibitor pazopanib for the reversal of memory and cognitive deficits in rat model neurodegeneration" http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2015/SC/c4sc03416c
DICP Researchers Made A New Progress in Theorytcial Investigation of Identification and Interaction between Biological Macromolecule and Small Molecular
By the media attention, Science and Technology Daily made a report on the front page on August 3 after the article was published, and followed by China Daily Chinese net, Chinese Academy of Sciences Web site and many other news media.
Recently, the Chemical Science published the 25 most downloaded articles in the third quarter (July - October) and our paper was ranked No. 9 in the above articles, with more than half of the extra attentions from Germany. Besides, in this quarter our article is also the most highly ranked articles from China!