Simultaneous conversion and storage of solar energy has been coming into the spotlight as a promising strategy for continuous utilization of solar energy. Solar rechargeable flow cell (SRFC) provides an attractive approach for in-situ capture and storage of intermittent solar energy via photoelectrochemical regeneration of discharged redox species for electricity generation. However, overall SFRC performance is restricted by inefficient photoelectrochemical reactions.
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) and Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy (DNL) research teams led by Prof. LI Can, Dr. SHI Jingying and Prof. CHEN Jian developed a solar rechargeable flow cell for in-situ solar energy capture and storage. They found an efficient SRFC based on a dual-silicon photoelectrochemical cell and a quinone/bromine redox flow battery for in-situ solar energy conversion and storage.
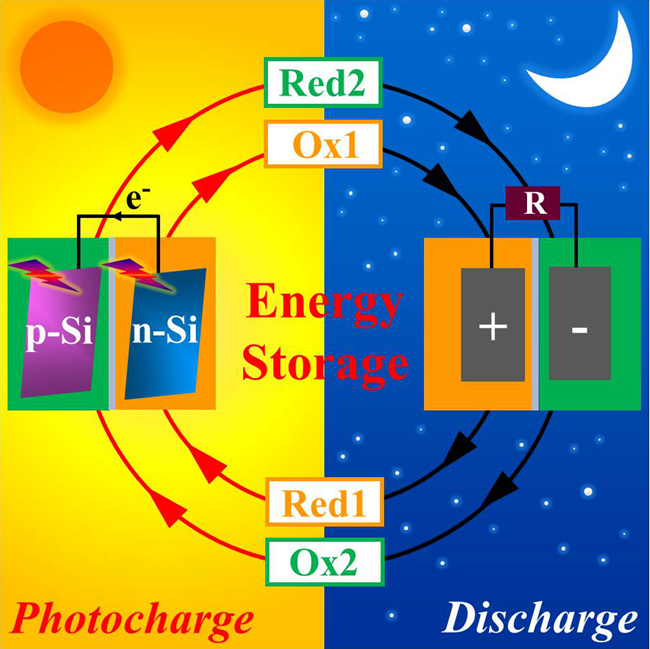
Researchers Develop a Solar Rechargeable Flow Cell for in-situ Solar Energy Capture and Storage (Image by LIAO Shichao and SHI Jingying)
Using narrow bandgap silicon for efficient photon collection and fast redox couples for rapid interface charge injection, the device shows an optimal solar-to-chemical conversion efficiency of 5.9%. It also exhibits an overall photon–chemical–electricity energy conversion efficiency of 3.2%. The proposed SRFC can be self-photocharged to 0.8 V and delivers a discharge capacity of 730 mAh-1. It may guide future designs for highly efficient solar rechargeable devices.
This work was published on Nature Communications (DOI:10.1038/ncomms11474). (Text/Image by LIAO Shichao and SHI Jingying)
Contact:
Dr. LU Xinyi
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
457 Zhongshan Road, Dalian, 116023, China,
Tel: 86-411-84379201,
E-mail: luxinyi@dicp.ac.cn